10. Making changes in a Fork#
As you may recall, a fork is a copy of a repository. Imagine you find a project on GitHub that you want to contribute to, but you don’t have permission to make changes to the original repository. In this case, you can fork the repository to create a copy of it in your GitHub account. You can then make changes to the forked repository and submit a pull request to the original repository to propose your changes.
10.1. Forking a repository#
To fork a repository, follow these steps:
Go to the repository you want to fork.
Click on the “Fork” button in the top right corner of the repository page.
Select your user account or organization where you want to fork the repository.
You can also choose if you want to fork all branches or just the default branch.
Wait for the forking process to complete.
You will be redirected to the forked repository in your account.
Note that the forked repository is an independent copy of the original repository. Any changes you make to the forked repository will not affect the original repository. In your forked repository, you will see a message indicating that it was forked from another repository.
10.2. Contributing from a forked repository#
After forking a repository, you can make changes to it like adding files, modifying files, etc. You can also create branches, make commits, and push changes to the forked repository.
To contribute your changes back to the original repository, you can create a pull request in the same way as before. When you create a pull request from a forked repository, GitHub will automatically detect that the pull request is coming from a fork and will give you the option to create the pull request to the original repository.
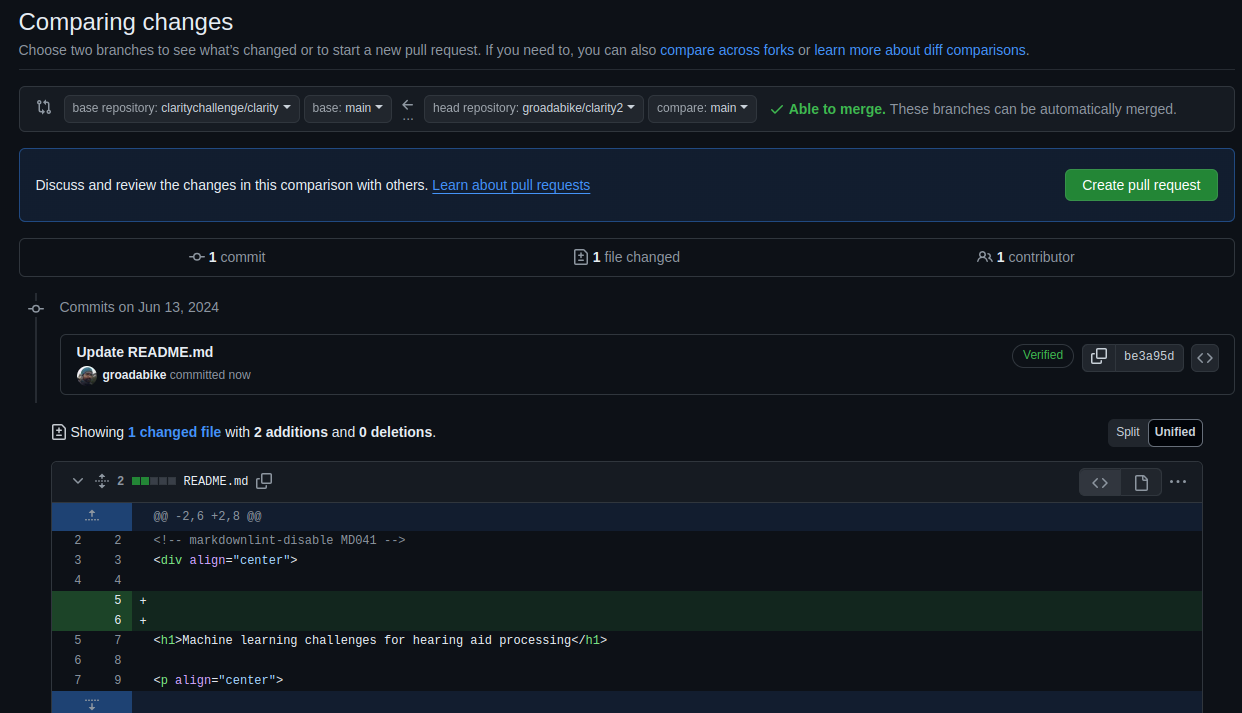
By following these steps, you can contribute to projects on GitHub even if you don’t have direct write access to the original repository.